Since the metaverse is a digital parallel world of the real one, the finance guard plans to move in. They also decided to move there because there are present currencies and people make trading, swaps, and make a profit. In fact, richness and wealth are being created also in the metaverse, where artwork is being sold and avatars are starting to have their own value. For that reason, finance guards are thinking about creating their own avatars. However, the Metaverse will need finance guards, rules, and controls like the real world. As a result, they will become a parallel finance guard, a parallel instrument to control and investigate even in this parallel world.
Why regulations are necessary in the metaverse
Moreover, the rights of the Metaverse must be protected, including economic and financial rights. Since the metaverse is a new and fast-evolving ecosystem, regulation is a problem. For this reason, governments and other institutions may struggle to keep up with technology and may not have the tools or resources needed to adequately control it. Therefore, this lack of monitoring might lead to issues like illegal conduct and even dangerous content.
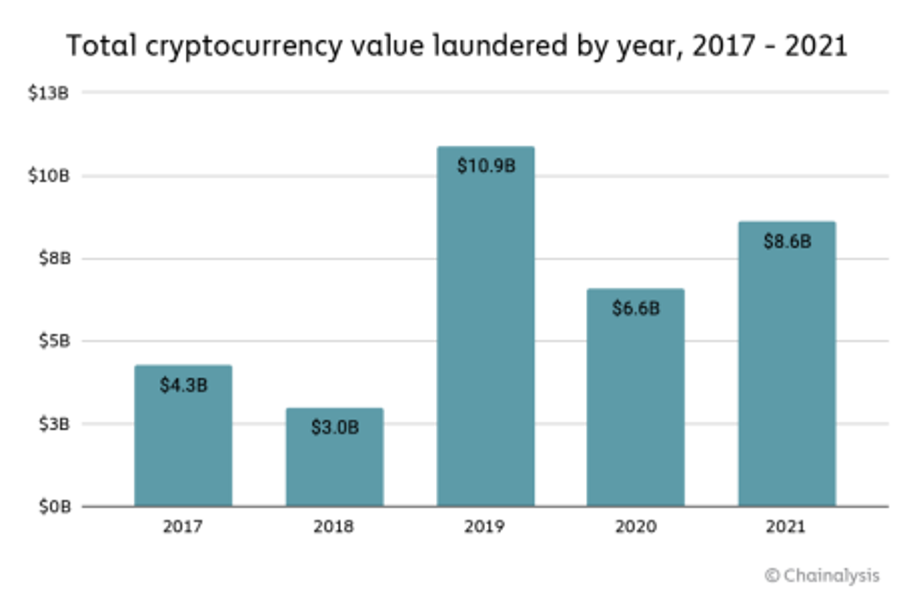
What’s more, in the metaverse, the avatars pay and receive cryptocurrencies that are the digital equivalent of a normal and tangible currency. Criminals also use cryptocurrencies as one of their tools for their misdeeds, such as money laundering. Even in the digital world, there is a money laundering profile that must be considered even if cryptocurrency is an alternative currency and it is also perfectly trackable.
For example, in fraud actions, criminals may leverage the anonymity and lax regulation of the metaverse to carry out scams. Apart from that, criminals could also create fake digital assets and sell them to unwary buyers, causing the victims to suffer financial loss.
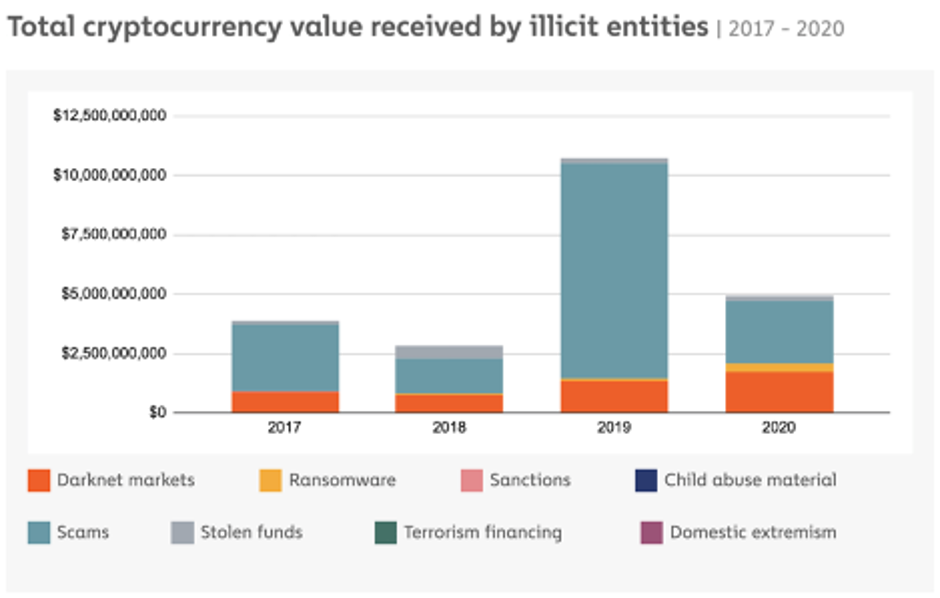
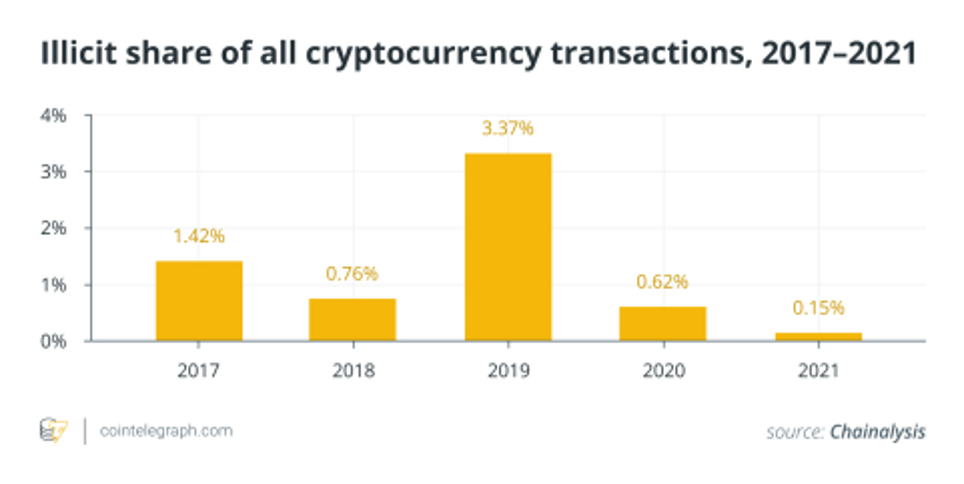
Example of irregularities in the metaverse
One real-world incident of cybercrime in the metaverse is the “Crypto Crime Cartel” case. Of course, we are talking about a group of cybercriminals. Founded in 2020, they had been operating in the metaverse in the virtual world of Second Life. In particular, they used a phishing scheme to mislead users into providing login and personal information. They then used that information to steal virtual currency and digital assets. Afterward, with the information they had obtained, the gang also committed financial crimes and identity theft in the real world. As a result, cryptocurrency money launderers successfully took digital assets and currencies worth millions of dollars.
Another example can be money laundering in the metaverse. This is a practice of using cryptocurrencies to hide the proceeds of criminal activities. One characteristic example is the sale of illicit drugs or weapons. This happens by concealing the source and ownership of the money through a complex web of transactions. So, the use of virtual goods or money to deceive investors into believing that their money is going toward a successful project is an example of financial fraud in the metaverse. However, in reality, the returns are being paid from the contributions of new investors rather than from any actual business gains. Moreover, crooks may utilize the metaverse to carry out financial transactions that are not disclosed to tax authorities in order to avoid paying taxes.
In conclusion, for all these reasons, a virtual finance guard must be present in the digital environment of the metaverse to avoid all these illegal actions and dangers.
Reference List
How to protect against crime in the metaverse
La Guardia di Finanza punta al Metaverso: “Faremo indagini anche lì con i nostri avatar”
