Introduction
About AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is a leading American semiconductor company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. AMD specializes in developing computer processors and related technologies for both business and consumer markets.
AMD‘s product portfolio includes microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, graphics processors, and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). These products serve a wide range of applications, including servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded systems.
Why AMD Matters to Investors
Looking forward, AMD’s potential to expand its footprint in selling graphics processing units (GPUs) to data centers presents a significant growth opportunity. This expansion could yield substantial gains for shareholders over the next decade.
The surge in demand for artificial intelligence (AI) hardware has pushed Nvidia‘s stock to new heights, and AMD could be on a similar path to success.
Purpose of this Blog
This blog explores AMD’s current market position, competitive advantages, future growth prospects, and why it could be a strong long-term investment.
You’ll gain insights into AMD’s innovations in the semiconductor industry, its competition with Intel and Nvidia, and its role in the rapidly growing sectors of gaming, data centers, and AI.
AMD’s Current Market Position
Market Leadership and Competition
In the AI stock universe, Nvidia currently dominates with over 90% market share in data-center GPUs and more than 80% in AI processors. However, AMD is positioning itself as a viable alternative.
While Nvidia has already advanced to the H200 and the new Blackwell platform, AMD and Intel are actively competing in the AI chip market.
AMD vs. Nvidia
Analysts are extremely bullish on Nvidia’s prospects in AI. Nvidia is expected to dominate the market for AI training due to its industry-leading combination of GPU hardware and the CUDA software platform. AMD, however, is projected to emerge as the second-largest player in data center GPUs behind Nvidia.
Despite Nvidia’s software advantage, which poses a significant challenge for AMD, analysts believe AMD will find a profitable niche in AI inference. AMD’s steady gains in server CPU share and its potential to win AI inference sockets in data centers are encouraging signs for investors.
However, some caution that AMD lags behind Nvidia in AI training and lacks a comprehensive software stack. Additionally, AMD’s PC and gaming businesses are more cyclical compared to Nvidia’s.
Yet, one key strength for AMD is that manufacturers prefer having multiple vendors to choose from, which prevents dependency on a single supplier. While Nvidia currently leads the market for GPUs used in computationally intensive AI workloads, AMD has proven itself as a capable fast-follower.
AMD vs. Intel
Intel is currently grappling with challenges stemming from a “technology gap” due to over a decade of underinvestment, as described by Intel CEO Patrick Gelsinger. AMD has been one of the primary beneficiaries of Intel’s manufacturing missteps.
Companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) and AMD have thrived as a result of Intel’s fumbles. While TSMC successfully navigated the 10nm and 7nm processes, AMD, a fabless semiconductor company, grew its share of the x86 server CPU market from almost zero to 23.9% through the first quarter of 2024.
Analysts remain optimistic about AMD’s continued gains in server CPU market share against Intel.
AMD’s Latest Innovations
AMD has been at the forefront of technological innovation in recent years. Below are some of AMD’s latest innovations and how they are shaping the future of technology.
The Rise of EPYC Processors for Data Centers
AMD’s EPYC processors have earned widespread acclaim for their performance and efficiency in data centers. Featuring up to 64 cores and 128 threads, these processors offer unmatched processing power for tasks such as cloud computing, virtualization, and other data-intensive applications.
By leveraging advanced technologies like PCIe Gen4 support and Infinity Fabric interconnects, EPYC processors deliver industry-leading performance while maintaining energy efficiency. This makes them an ideal choice for businesses seeking to optimize their data center operations.
Advancing Security with AMD Infinity Guard
Security is a top priority in today’s digital world. To address this need, AMD introduced Infinity Guard, a suite of security features designed to protect sensitive data and ensure system integrity.
From hardware-enforced security measures to advanced encryption technologies, Infinity Guard offers comprehensive protection. By integrating these features into their products, AMD is helping organizations stay ahead of potential security threats.
AMD’s innovations are driven by cutting-edge research and development, focusing on delivering high-performance solutions for both consumers and businesses.
Financial Analysis
P/E Ratio
The Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio measures the relationship between a company’s stock price and its earnings per share. Companies with a P/E ratio over 30 or a negative one are generally considered “growth stocks,” meaning that investors expect the company to grow or become profitable in the future.
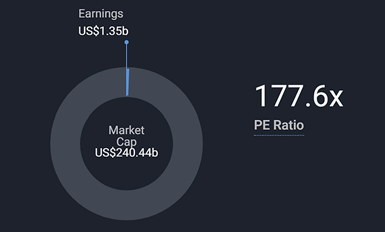
(The above table displays AMD’s Price to Earnings ratio, calculated by dividing AMD’s market capitalization by its current earnings.)
Future Growth
Advanced Micro Devices is forecasted to grow its earnings by 39.4% and revenue by 17.8% per year. Earnings per share (EPS) is expected to increase by 39.3% per year, and return on equity is projected to be 15.9% within three years.
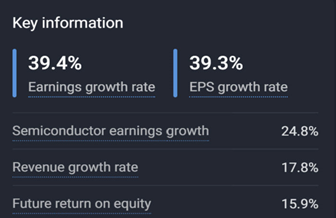
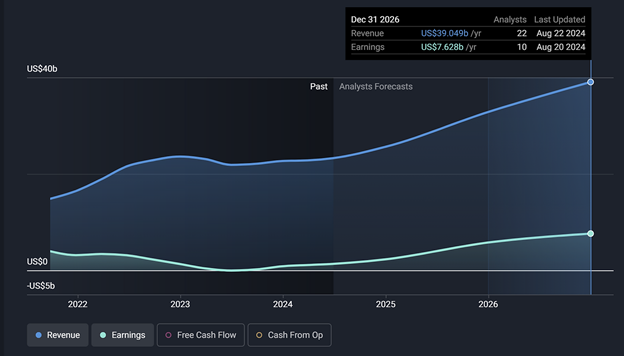
Earnings and Revenue Growth Forecasts
The chart illustrates AMD’s revenue and earnings trends from 2022 through 2026, alongside analysts’ forecasts. The blue line, representing revenue, shows steady growth, especially towards the end of the forecast period in 2026, where AMD’s revenue is projected to reach approximately $39.049 billion annually.
The green line, representing earnings, reflects a similar upward trend, despite a dip around 2023. By 2026, AMD’s earnings are expected to recover and rise to $7.628 billion annually.
This chart indicates that although AMD faced challenges in 2023, both revenue and earnings are anticipated to grow significantly in the coming years. Analysts are optimistic about AMD’s financial performance, expecting strong growth, particularly in revenue, which is projected to increase more rapidly than earnings. This outlook suggests a promising future for AMD.
Risks and Uncertainty
The AI opportunity for both Nvidia and AMD is immense but still in its early stages. Forecasting growth in such a dynamic market is challenging. If enterprise adoption of AI is slower than expected or if hyperscalers shift workloads to in-house chips, growth estimates could be impacted.
Geopolitical tensions surrounding AI and potential export restrictions also pose risks. Nvidia’s gaming business, which can be volatile due to factors like crypto demand and chip shortages, adds another layer of uncertainty. Similarly, AMD has exposure to the cyclical PC market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both AMD and Nvidia are well-positioned to benefit from the AI megatrend, Nvidia currently has the upper hand due to its market leadership, software advantages, and explosive growth trajectory in the near term.
Nevertheless, AMD is expected to carve out a profitable niche in AI inference and continue gaining share in server CPUs. Catching up to Nvidia in AI training will be challenging, but AMD remains a significant player in oneS of the most transformative technologies of our time, offering a long runway for growth.